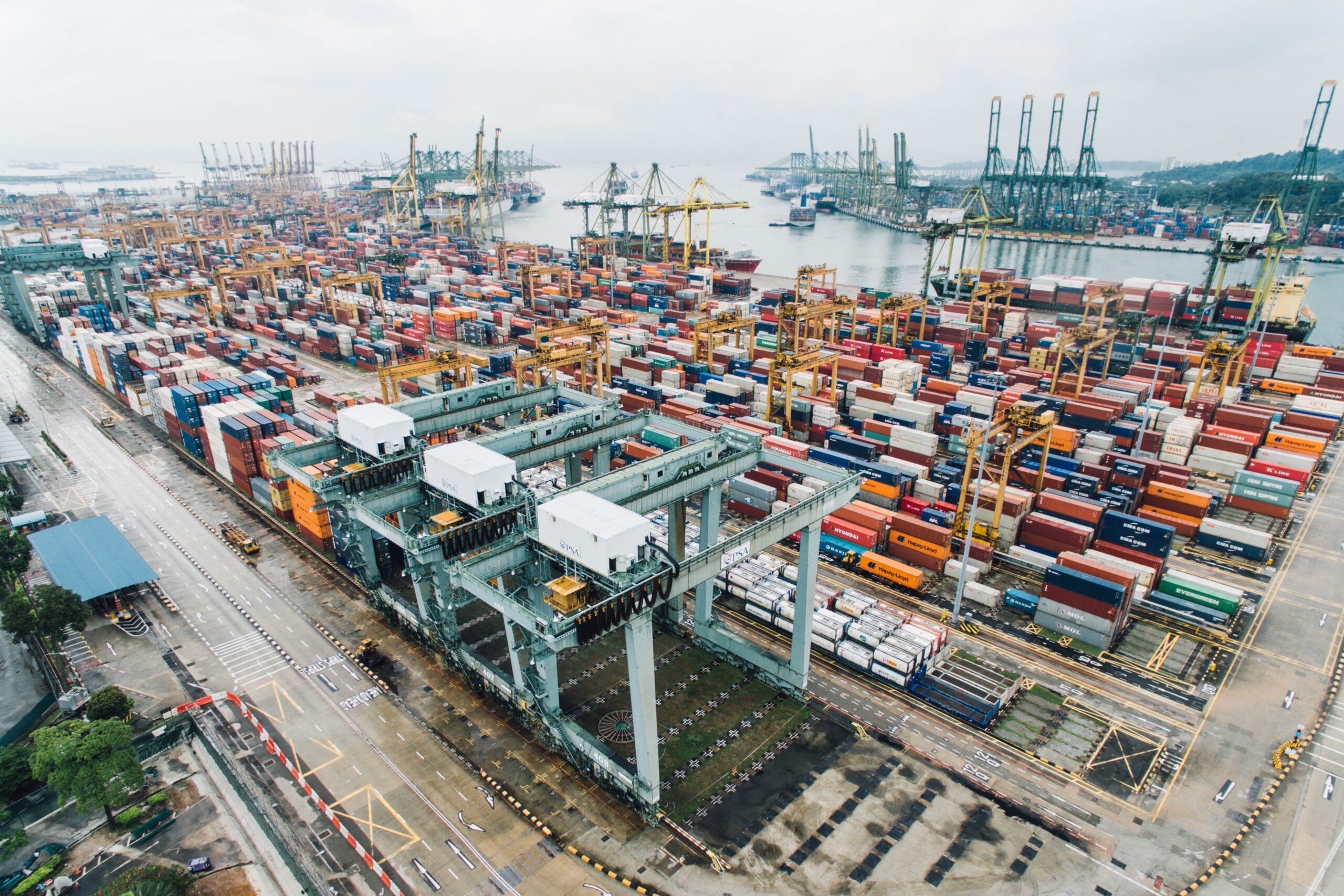
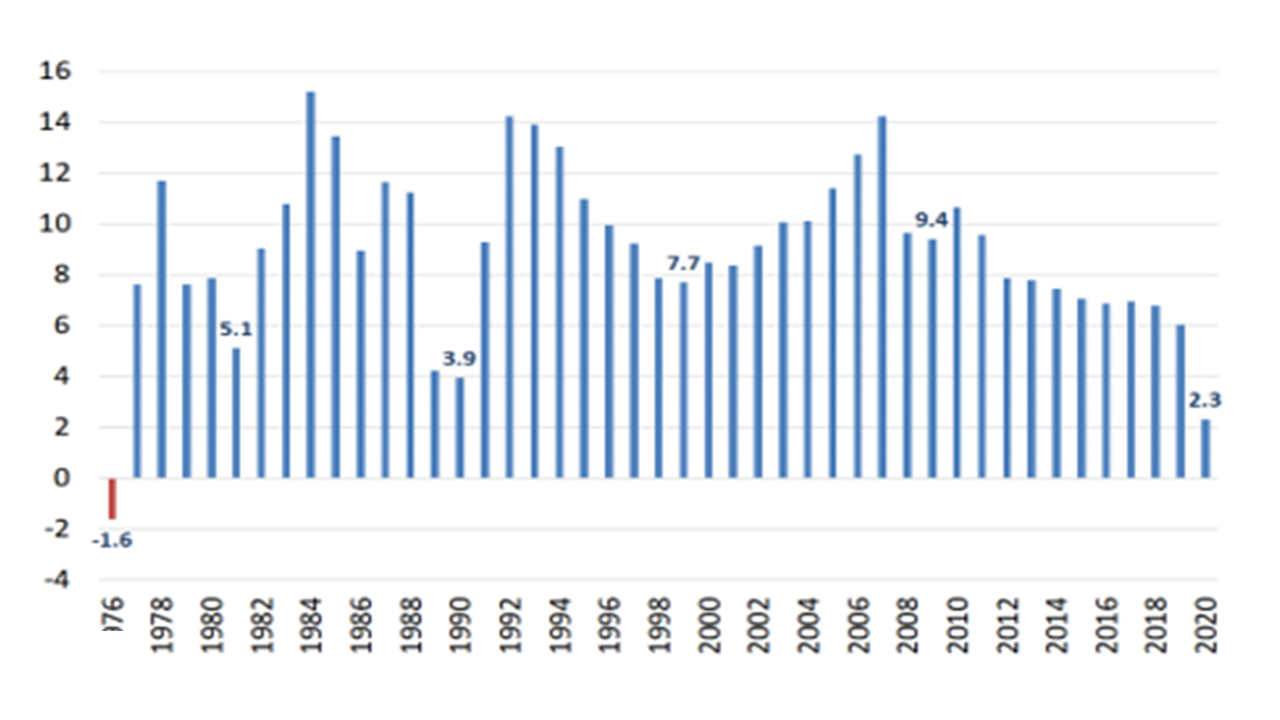
The debate on the viability of industrial policy design based on the fragmentation of global value chains, from a cost optimization perspective, did not arise first in the wake of the Covid-19 crisis but was present long before. This industrial policy design was justified by the great development of logistics and transport across the world’s industrial clusters, which allowed just-in-time manufacturing to become the main adopted production model. However, the disruption of logistics supply chains after the advent of the crisis has multiplied the voices calling for a review of the current model of the organization of value chains, in favor of reshoring or nearshoring. This widely shared perception remains rather unconfirmed by the facts. Indeed, it has been observed that the economic sectors that are most integrated into global value chains have experienced a faster recovery than the remaining sectors, which would mean that integration into global value chains can be a factor that accelerates recovery, and therefore guarantees resilience in the event of a major economic shock.