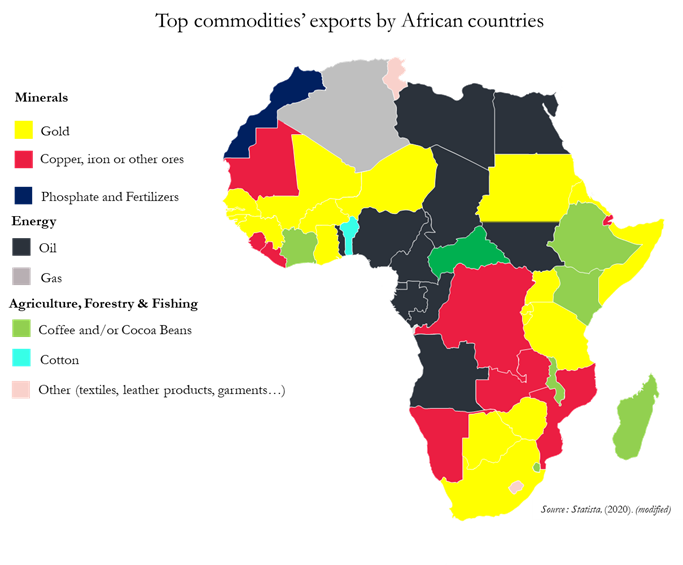
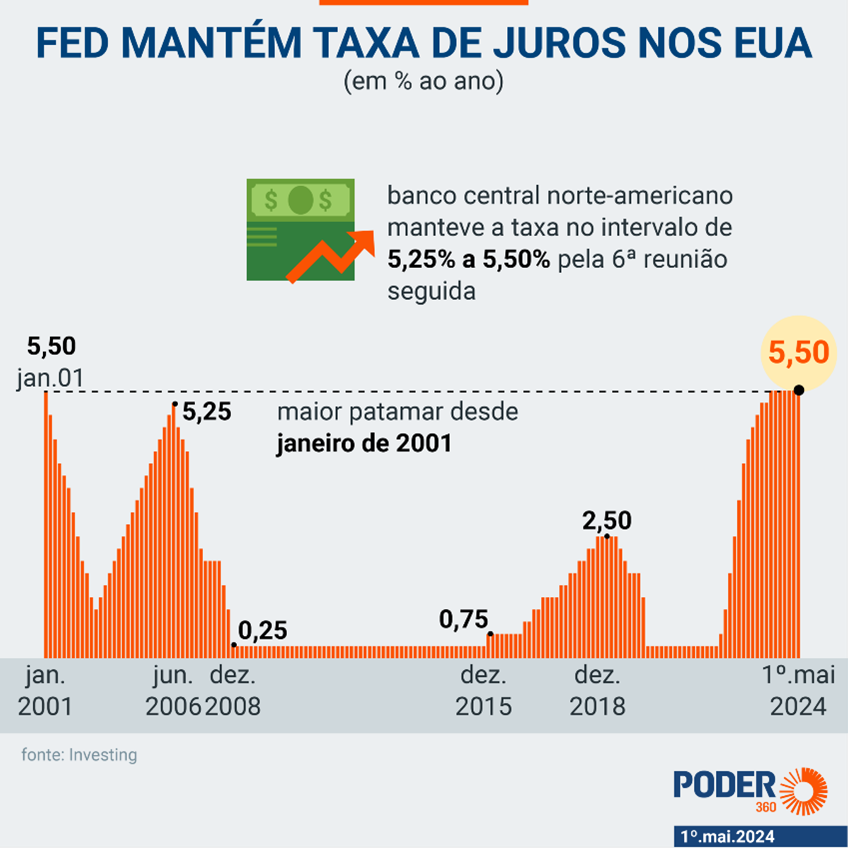
(Videos) Global Economy + Digital Currencies
The global economy is expected to stabilize for the first time in three years, but more weakly than in previous recoveries, according to a new report from the World Bank. Inflation, higher interest rates, as well as trade and geopolitical tensions could make this decade more sluggish than the last one ------------- Explore the evolution, impact, and future trends of digital currencies with our Senior Fellow, Mr. Otaviano Canuto. In this insightful video, he sheds light on how digital currencies are transforming global markets and what to expect in the coming years.